Identity federation (IDF) is an architecture where identities of an external identity provider (IDP) are recognized. Single sign-on (SSO) is where the credentials of an external identity are used to allow access to a local system (e.g., AWS).
Types of IDF include:
- Cross-account roles: A remote account (IDP) is allowed to assume a role and access your account’s resources.
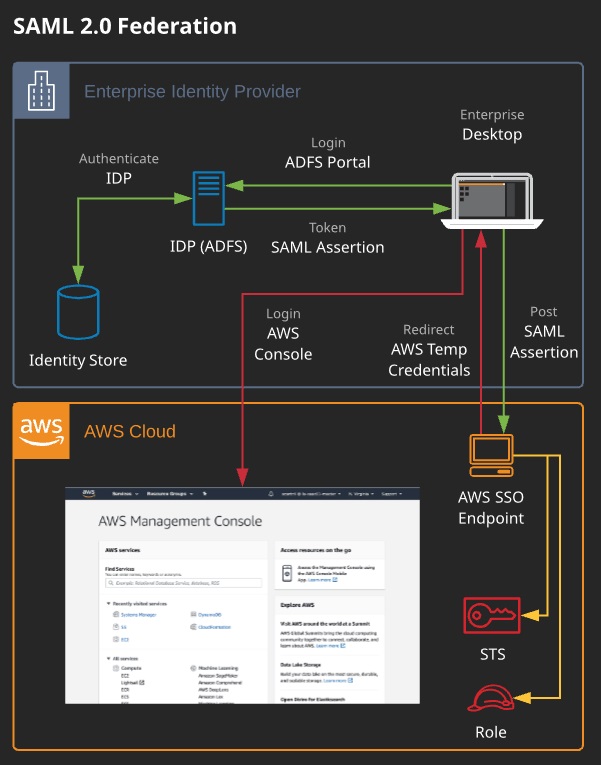
- SAML 2.0 IDF: An on-premises or AWS-hosted directory service instance is configured to allow Active Directory users to log in to the AWS console.
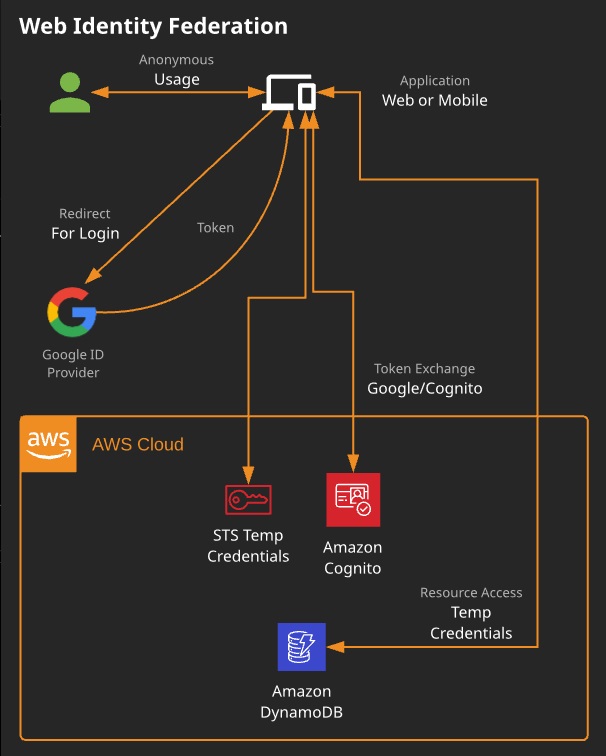
- Web Identity Federation: IDPs such as Google, Amazon, and Facebook are allowed to assume roles and access resources in your account.
Cognito and the Secure Token Service (STS) are used for IDF. A federated identity is verified using an external IDP and by proving the identity (using a token or assertion of some kind) is allowed to swap that ID for temporary AWS credentials by assuming a role.
Federation: Providing a non-AWS user temporary AWS access by linking that user’s identity across multiple identity systems
Federation with Third-Party Providers:
- Most commonly used in web and mobile applications
- Amazon Cognito allows for creation of unique identities for users
- Uses identity providers to federate them Facebook, Google, Amazon, etc.
Establishing Single Sign-On (SSO) Using SAML 2.0:
- Most commonly used in enterprise environments with an existing directory system Active Directory, etc.
- Federated users can access AWS resources using their corporate domain accounts
- Federation also aids user management by allowing central management of accounts

